
The movement is caused by the addition or subtraction of a constant from a function. Horizontal Compression - Properties, Graph, & Examples. Other factors include topography, crustal thickening/thinning. Shear stresses develop at transform boundaries.

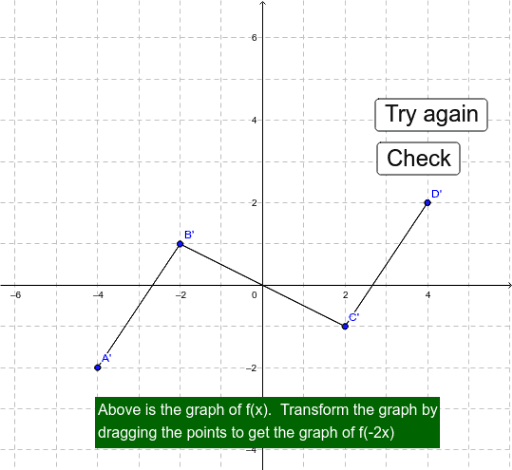
The four main types of transformations are translations, reflections, rotations, and scaling.Ī translation moves every point by a fixed distance in the same direction. A horizontal compression looks similar to a vertical stretch. Divergent plates decrease horizontal compression. 12.2 DEFINITIONS ( a ) Effective length : The vertical distance between the. Stresses in horizontal direction are very often different to the stress in vertical direction. This change will cause the graph of the function to move, shift, or stretch, depending on the type of transformation. 12.1 INTRODUCTION Compression members are structural elements primarily. Vertical (effective) stress is not enough to define the state of stress in a solid.
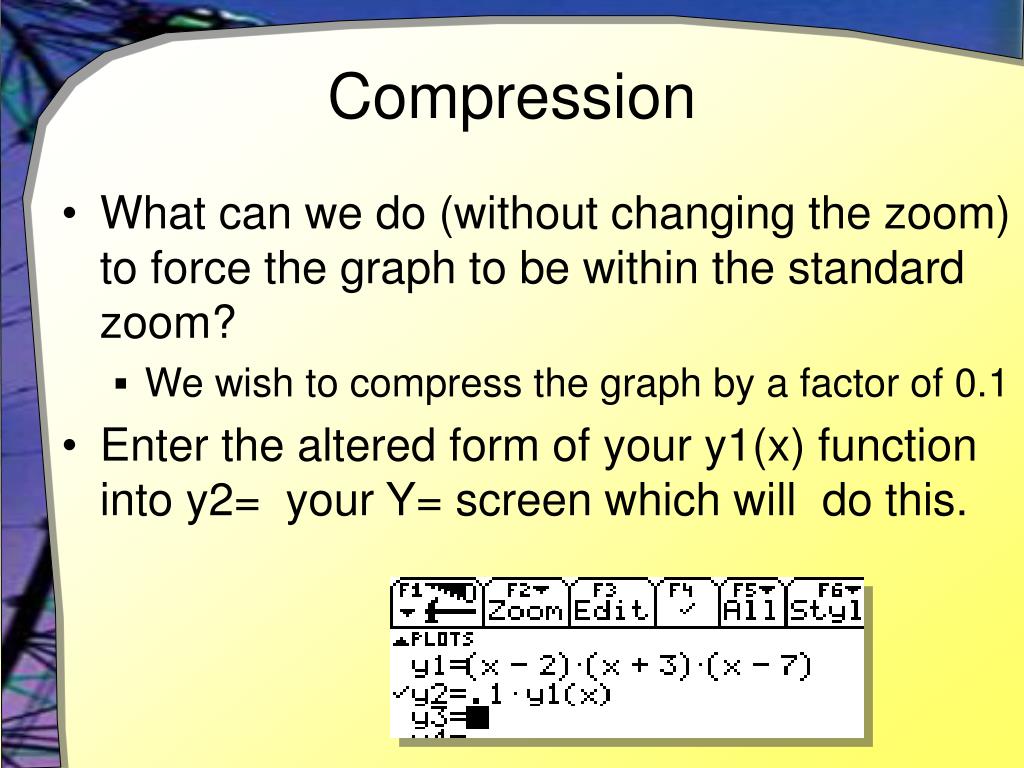
Transformations often preserve the original shape of the function. Note that (unlike for the y-direction), bigger values cause more compression.Suppose a scientist is comparing a population of fruit flies to a population that progresses through its lifespan. Arch foundations must therefore prevent both vertical settling and horizontal sliding. Example: Graphing a Horizontal Compression. If your application needs to handle all events with no compression, you can unset this attribute. Four types of stresses affect the Earth’s crust: compression, tension, shear and confining stress. When the plates are pulled or pushed together, stress occurs. The crust is broken into several parts, known as the continental plates.
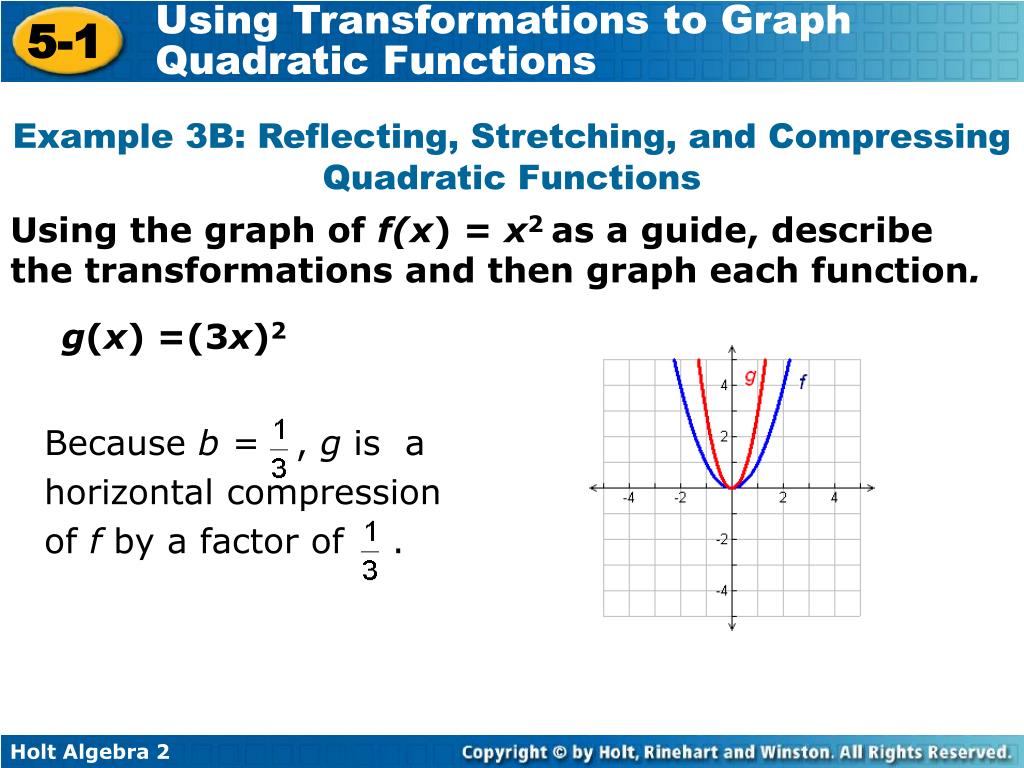


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
